Blog / How has 3D Printing in Healthcare become a Prescription for the Future?

Monday, 5 Mar 2018
How has 3D Printing in Healthcare become a Prescription for the Future?
3D printing in Healthcare was determined when a five-month-old girl from Karnataka was diagnosed with craniosynostosis. The problem is described as two bones of her skull were fused together that hinder the development of her brain.
To solve this, a team of doctors at Sakra World Hospital in Bengaluru performed the “skull expansion” surgery separating the bones in the deformed skull. Post-Operation, the doctors made use of a helmet for hindering the growth in the particular direction. Usually, such helmets are made in the U.S. that costs about 1.5 – 2 lakhs but the Bengaluru-based company did the miracle by making it for just ₹ 20,000.
Ostedo3d Initiative: 3D printing in the healthcare industry
The startup, Ostedo3d has customized the helmet for this infant using 3D printing technology. Today, they design and fabricate 3D-printed pre-surgery models for dentistry, neurosurgeries, and maxillofacial surgeries. In addition to it, they have assisted doctors in over 350 cases across India. 3D printing allows doctors to touch it, feel it, and know exactly where the problem lies which results in increased accuracy during surgeries.
The team also developed a proprietary cloud-based platform for the doctor to upload CT scans and MRI records of patients. In a few minutes, it presents them with a three-dimensional image of patient’s anatomy.
How does it work?
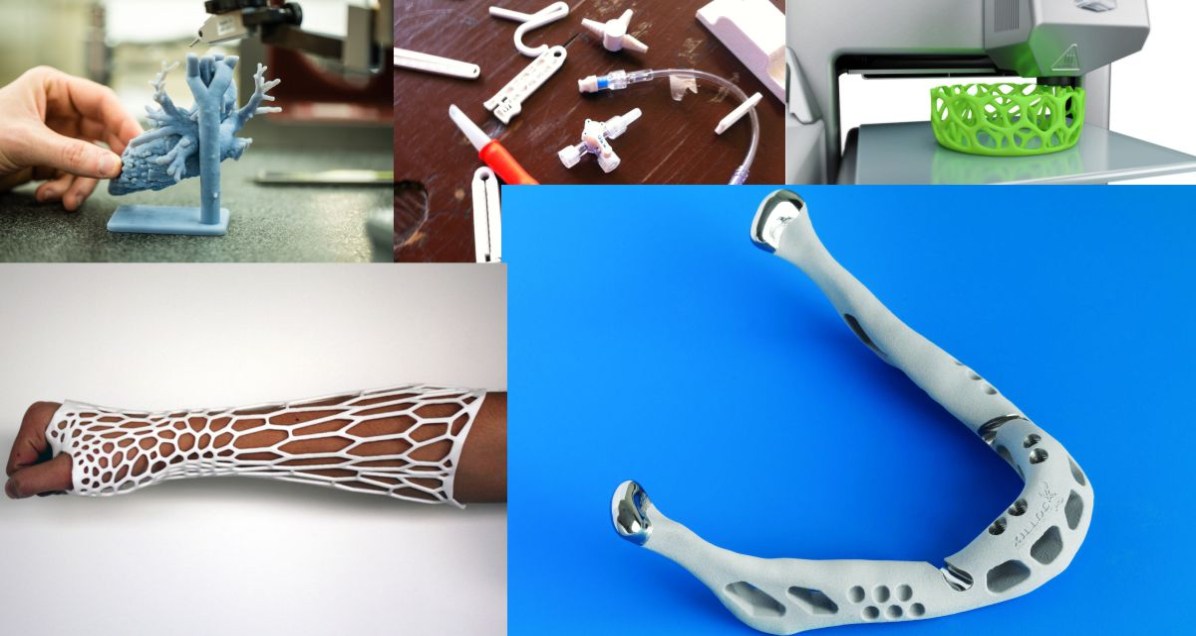

Osteo3d’s custom-made 3D printed surgical guide’ enables surgeons to achieve a greater level of precision. It fits like a glove on the part of the body which the doctor’s need to cut. There are lines that guide doctor about where to make the incision and regarding biocompatible materials. The startup also fabricated the customized 3D printed cranial flaps for recognizing a particular defect in the skull.
Challenges and Limitations:
Despite its transformative potential, 3D printing in healthcare faces several challenges and limitations. Regulatory hurdles are significant, as obtaining the necessary approvals and certifications for 3D-printed medical devices can be complex and time-consuming. The high cost of 3D printing technology and materials poses a barrier to widespread adoption, particularly in resource-limited settings. Technical constraints also exist, with current 3D printing technologies limited by material properties and difficulties in scaling production. Additionally, there is a pressing need for specialized training for healthcare professionals to effectively use these technologies. Ethical concerns, especially related to bioprinting and patient safety, further complicate the landscape, requiring careful consideration and ongoing research.
Future Trends in 3D Printing in Healthcare
The future trends in 3D printing in healthcare are both exciting and promising. Advances in material science are expected to introduce new biocompatible materials, enabling more sophisticated and functional 3D-printed medical solutions. Bioprinting is making strides toward creating complex tissues and even organs, which could revolutionize regenerative medicine. Integration with artificial intelligence (AI) is set to enhance design accuracy and streamline the printing process, making custom solutions more efficient. Personalized medicine will see significant growth, with 3D printing allowing for tailored implants and devices that meet individual patient needs. Global expansion of 3D printing technologies is anticipated to increase accessibility and adoption, bringing advanced healthcare solutions to underserved regions.
Impact on Patient Outcomes and Cost Efficiency
The impact of 3D printing on patient outcomes and cost efficiency is profound. By providing highly customized medical devices and implants, 3D printing can lead to improved patient outcomes through enhanced fit and functionality. Surgical precision is increased with 3D-printed guides and models, reducing complications and recovery time. Moreover, the ability to produce cost-effective solutions on-demand can significantly lower healthcare expenses. For example, 3D-printed implants and prosthetics can be produced at a fraction of the cost of traditional methods, making advanced care more affordable and accessible. Overall, 3D printing not only promises better clinical results but also offers a pathway to more economical healthcare solutions
Gaining Recognition by the Government
The startup has so far built a network of 120 doctors who ultimately rely on startup services. According to doctors, Osteo3d is entirely inclined towards clinical practices, as it has crossed 350-plus cases. Based on the successful completion of cases, it had received around ₹ 50 lakhs from the Indian Government’s Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Control in February 2015. In addition to it, the Karnataka government also granted ₹40 lakhs to Osteo3d under its idea-to-proof-of-concept fund for biotech startups.
Though 3D printing technology is well established, and it has proven successful in healthcare, its adoption is not widespread. This is because of the lack of awareness among doctors and patients. Doctors are spreading the impact and benefits of the concept, and thus, 3D printing in healthcare undoubtedly remain prescription for the future.
Conclusion
3D printing is transforming healthcare by addressing key challenges and paving the way for innovations in patient care. Although there are hurdles such as regulatory issues and high costs, advancements in materials, bioprinting, and AI are enhancing precision and affordability in medical solutions.
For those eager to excel in this evolving field, Dreamzone’s Master Diploma in 3D Modeling & Animation provides essential training in 3D printing technologies. This program equips students with the skills needed to thrive in the future of healthcare and beyond.

Corporate Headquarters
No. 25, Dr. Radhakrishnan Salai, Mylapore,
Chennai - 600 004, Tamil Nadu, India.
+91 98843 85048
Flagship Events
Trending Courses
Fashion Design
Interior Design